DNS MX Record
P.Leclercq in Security 2023-11-10 technology

The DNS MX record
The DNS MX Record: how your mail finds its target.
The email journey to the recipient
In a previous article, we have represented the email journey.
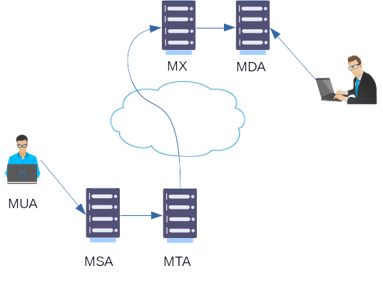
And we have defined the MX: Mail eXchange as the destination MTA. The question we will answer now is: how does the mail transfer agent find the destination (MX)?
The DNS MX record
In a precedent article, we have also described a part of the DNS system, namely the translation of a machine or application into an IP address, and the hierarchy of domain names and subdomains.
But DNS can distribute other information pertaining to a domain name. Each type of attribute DNS can contain is characterized by a DNS record type. These records are stored in the DNS server designated for the domain.
One of the DNS record types is the MX record. It specifies the name of a mail server responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain name. There can be several MX records for a domain as there can be several mail servers (several servers in a cluster or main and backup servers).
The syntax of a DNS MX record is the following:
<domain> <TTL> <class> <type> <priority> <hostname>
Example:
google.com. 300 IN MX 10 smtp.google.com
- <domain> is the domain name for which the server is the mail server. All mails targeted at <user>@google.com will land on this server.
- <TTL> is the time to live of the distributed information. Every machine who has queried the MX record for the domain can keep the information cached locally for this number of seconds. Afterwards, it has to re-query DNS again.
- <class> is the kind of network this record is relevant for. For the moment, there is only one class defined: IN (=Internet).
- <type> is the record type; in our present case it is a MX record.
- <priority> is a number indicating the preference where the mails must be sent to. The lowest the number, the highest the preference. For example, if a domain has 2 mail exchangers, one with a priority of 10 and the other one with a priority of 20, the mail sender will first try to send the email to the first one (priority 10), and if it fails then to the second one (priority 20).
- <hostname> is the name of the mail server for the domain.
This is how a mail agent can find where it has to send an email to somebody@google.com: the destination machine is in the MX record.
How to find the MX record for a domain
-
On Windows, the utility to query DNS is
nslookup.
The command to query a MX record is:
nslookup -type=mx <domain>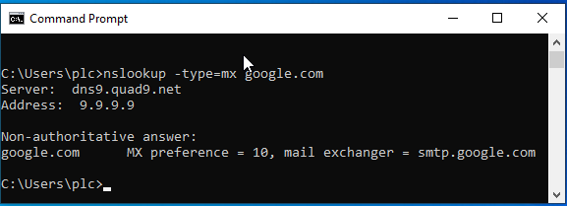
-
On Linux:
-
The same
nslookupcommand can also be used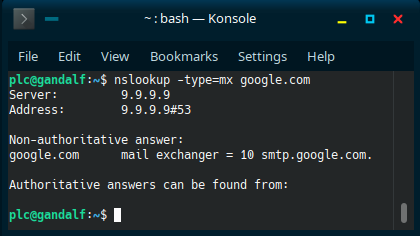
-
A more modern and versatile utility is
dig.
The command is:dig -t mx <domain>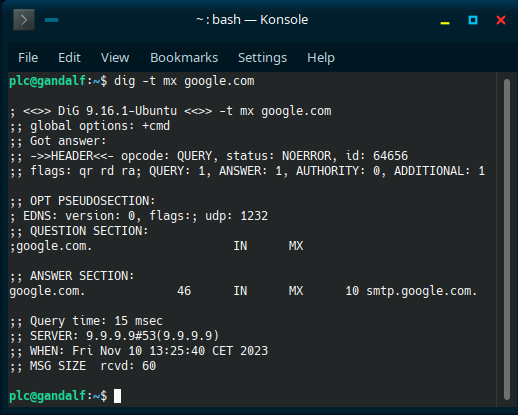
-
-
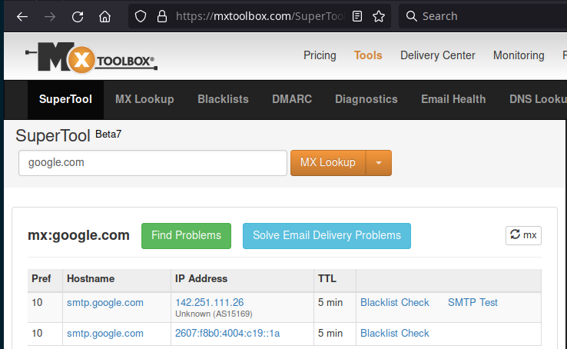
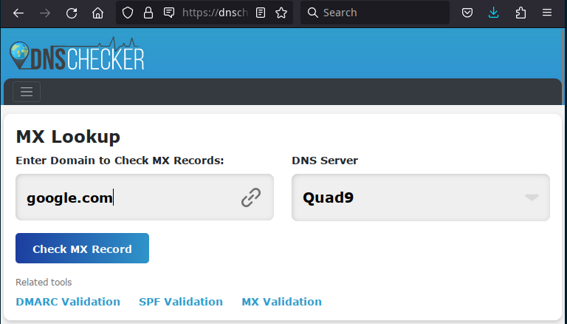
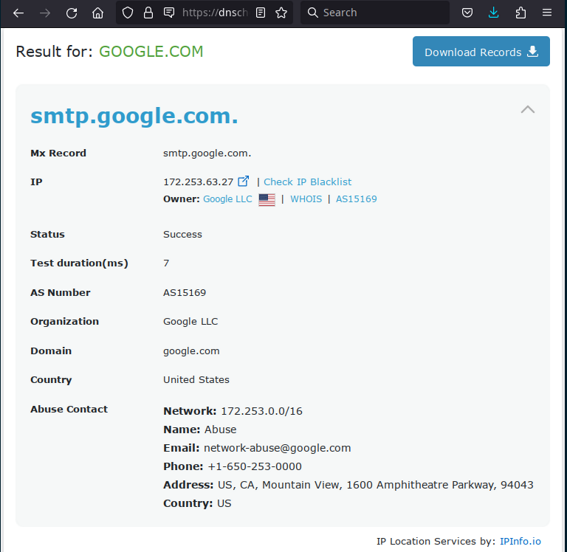
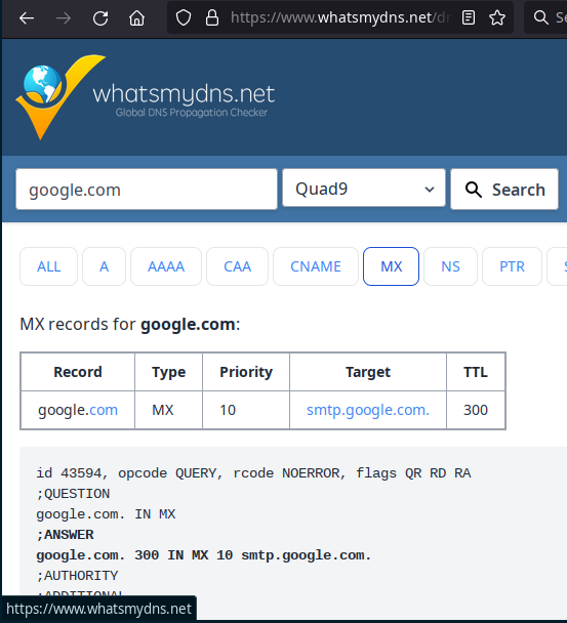
On the web, there are several sites available to display MX records: